
How 3D printing supports educators
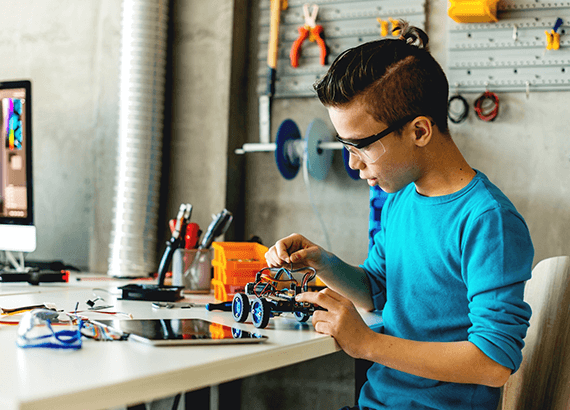
A student working with 3D printed educational aids.
Educators face three major challenges in their work
-
Skills sought after in the job market evolve faster than their curriculums
-
Customized educational aids are expensive and take a long time to fabricate
-
Shortages in educational aids or equipment lead to lower pass rates
Tailored educational aids
3D printers can print almost all shapes, so educational aids can be designed specifically for a given curriculum.
Predictable costs
Models of different designs can be fabricated at a steady price in a predictable time.
Creative freedom
Engineering students can use 3D printers to build physical models of their own design and interact with them.
Higher pass rates
3D printers make it possible to offer sets of educational aids to each individual student which increases the pass rates.
Workflow in using 3D printing educational aids
Educators can implement 3D printers in their work following four simple steps. Here's how it works.

Step 1: Curriculum development
A curriculum is designed to maximize student learning outcomes.

Step 2: Design courses
A course teaching CAD software and design principles is developed.
Step 2: CAD design
Educational aids for the curriculum are designed in CAD software.


Step 3: Practical classes
Students use available 3D printers to fabricate their own designs.
Step 3: 3D printing
Models are 3D printed in-house on an on-demand basis.


Step 4: Discussion
Students can see how their designs work in real world and discuss it with the teacher.
Step 4: Flexible adjustments
Additional educational aids can be quickly printed as new students sign up for a course.
Step 4: Discussion
Students can see how their designs work in real world and discuss it with the teacher.

Step 3: Practical classes
Students use available 3D printers to fabricate their own designs.

Step 2: Design courses
A course teaching CAD software and design principles is developed.

Step 1: Curriculum development
A curriculum is designed to maximize student learning outcomes.

Step 2: CAD design
Educational aids for the curriculum are designed in CAD software.

Step 3: 3D printing
Models are 3D printed in-house on an on-demand basis.

Step 4: Flexible adjustments
Additional educational aids can be quickly printed as new students sign up for a course.
3D printers for education
Additive manufacturing is a technology than can benefit educators in one of two ways. First, personalized educational aids can be 3D printed on demand. Second, 3D printers themselves can work as educational aids in classrooms.

A set of bones 3D printed as educational aides for anatomy students
at the Victoria University in Melbourne, Australia.
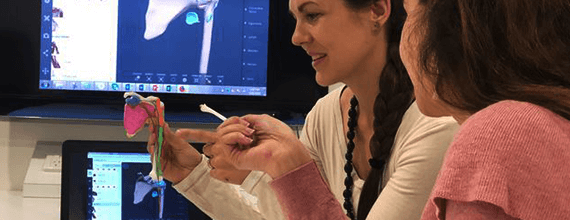
Anatomy classes with 3D printed educational aids at the Victoria University
in Melbourne, Australia.

Students at a primary school
attending a 3D printing class.
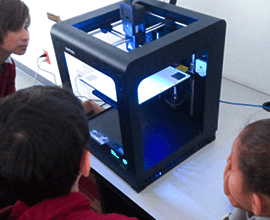
3D printer used at a technology
course at a primary school.

Students working with 3D printers
at a basic engineering course.
3D printing technologies for education
The choice of the right 3D printing technology for a school or a university depends on the projected size and number of the models.

Parts with complex geometry
Resin 3D printing technologies like the Zortrax UV LCD are best for small yet complex products made in high quantities.
See more
Parts with simple geometry
LPD technology is the most cost-efficient for making simple medium size models in large quantities.
See more
Parts with complex internal geometry
LPD Plus technology is best for intricately designed, medium size details with complex internal architectures like anatomical models.
See more
High-quality end-use products
SVS automated post-processing devices can be used with LPD or LPD Plus printers to make water-tight models with superior aesthetics.
See moreOur Users stories
Read more about the impact 3D printing technology has on businesses that have implemented it already.