3D Printing Materials for Automotive Industry Applications
3D printing technology is commonly used in automotive industry with nearly all major manufacturers having additive manufacturing systems already implemented at factories and design centers. Below is a brief overview of the most widespread 3D printing materials used at both prototyping and manufacturing stages in an automotive product cycle.
A cost-efficient 3D printing material for automotive: Z-ABS
Z-ABS is a 3D printing filament compatible with nearly all Zortrax extrusion-based 3D printers like the M200 Plus, M300 Plus, or M300 Dual. The material is based on standard acrylonitrile butadiene styrene which is one of the most popular plastics in use today.
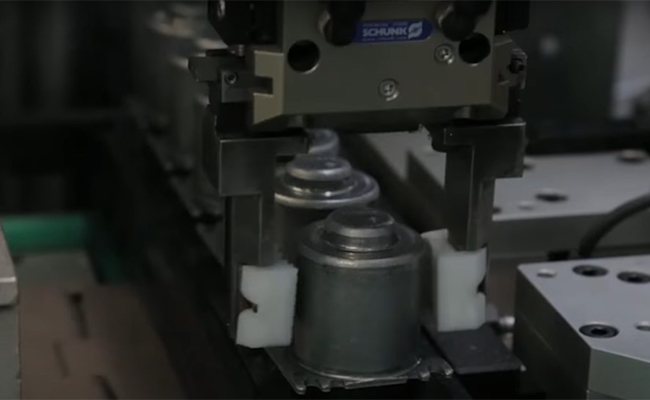
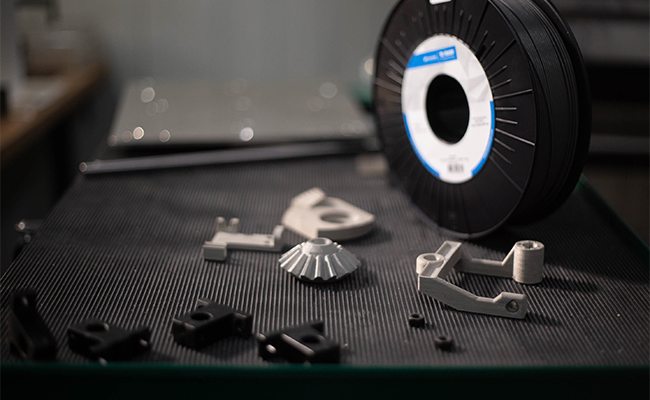
Because the material is so widespread and can be processed by nearly all 3D printers, it is one of the most cost-efficient options for making 3D printed parts. This is why multiple automotive manufacturers like Toyota print their early prototypes out of Z-ABS. This way, multiple iterations of a design can be made in a budget-friendly manner. Moreover, there are cases where Z-ABS thermal and mechanical properties are enough for end-use parts. One example from Toyota’s factory in Poland is a valve lever cover used to hold valve levers in place when the engine is moved from one assembly line to another. According to Toyota engineers, the lifespan of this jig made with Z-ABS on the Zortrax M300 Plus 3D printer can be as long as 6 months.


A high-temp filament for automotive applications: BASF Ultrafuse® PP GF30
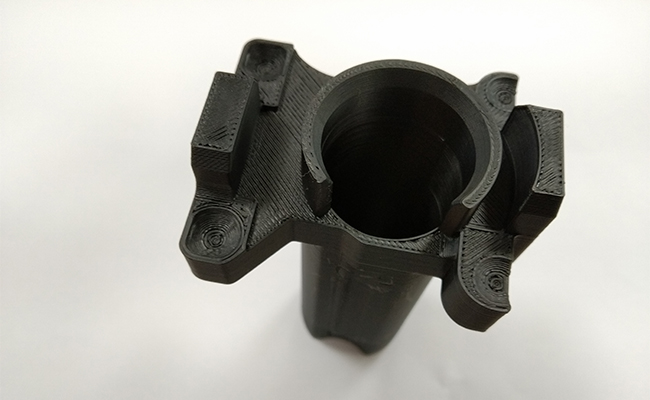
BASF Ultrafuse® PP GF30 is a polypropylene reinforced with 30% of glass fiber. It is one of the most used polymers in cars – nearly all under the hood components in almost every vehicle are made with it. To deliver the capability to 3D print with PP GF30 Zortrax partnered with BASF, one of the largest chemical companies in the world, to calibrate their BASF Ultrafuse® PP GF30 filament on the Zortrax M300 Dual 3D printer.
Parts 3D printed on the Zortrax M300 Dual with BASF Ultrafuse® PP GF30 can operate in the same range of temperatures as the molded PP GF30 components installed as stock in most cars. The material retains its properties in freezing cold exceeding -20 ºC and in heat reaching 120 ºC. That is why an automotive part 3D printed with BASF Ultrafuse® PP GF30 can safely endure in a vehicle left outside in winter without becoming excessively brittle and withstand high temperatures under the hood when the engine is running.
Such properties enable using parts 3D printed with BASF Ultrafuse® PP GF30 in multiple scenarios. At the prototyping stage, such parts can be used in demo cars and even in short-series, pre-production vehicles used for long-range and environmental tests. At the manufacturing stage, BASF Ultrafuse® PP GF30 can be used to 3D print production jigs and fixtures that need to retain their high rigidity in a wide range of temperatures. Smaller workshops can also use this material to 3D print spare under the hood components that are no longer in production or are unavailable for other reasons.